Insights-Driven Product Strategy
A strong product strategy is not built on assumptions or gut feelings — it must be driven by insights.
As Jeff Bezos famously stated, “No customer ever asked Amazon to create the Prime Membership program.” Instead, Amazon identified patterns, behaviors, and opportunities that led to one of its most successful innovations. True innovation often comes from understanding customers deeply, rather than simply responding to direct requests.
To create a truly impactful and data-driven product strategy, companies must establish a continuous and collaborative approach to collecting, generating, and sharing insights across teams. This ensures that product decisions are rooted in real data, customer behavior, and market trends, rather than opinions or isolated feedback.
The Role of Insights in Product Strategy
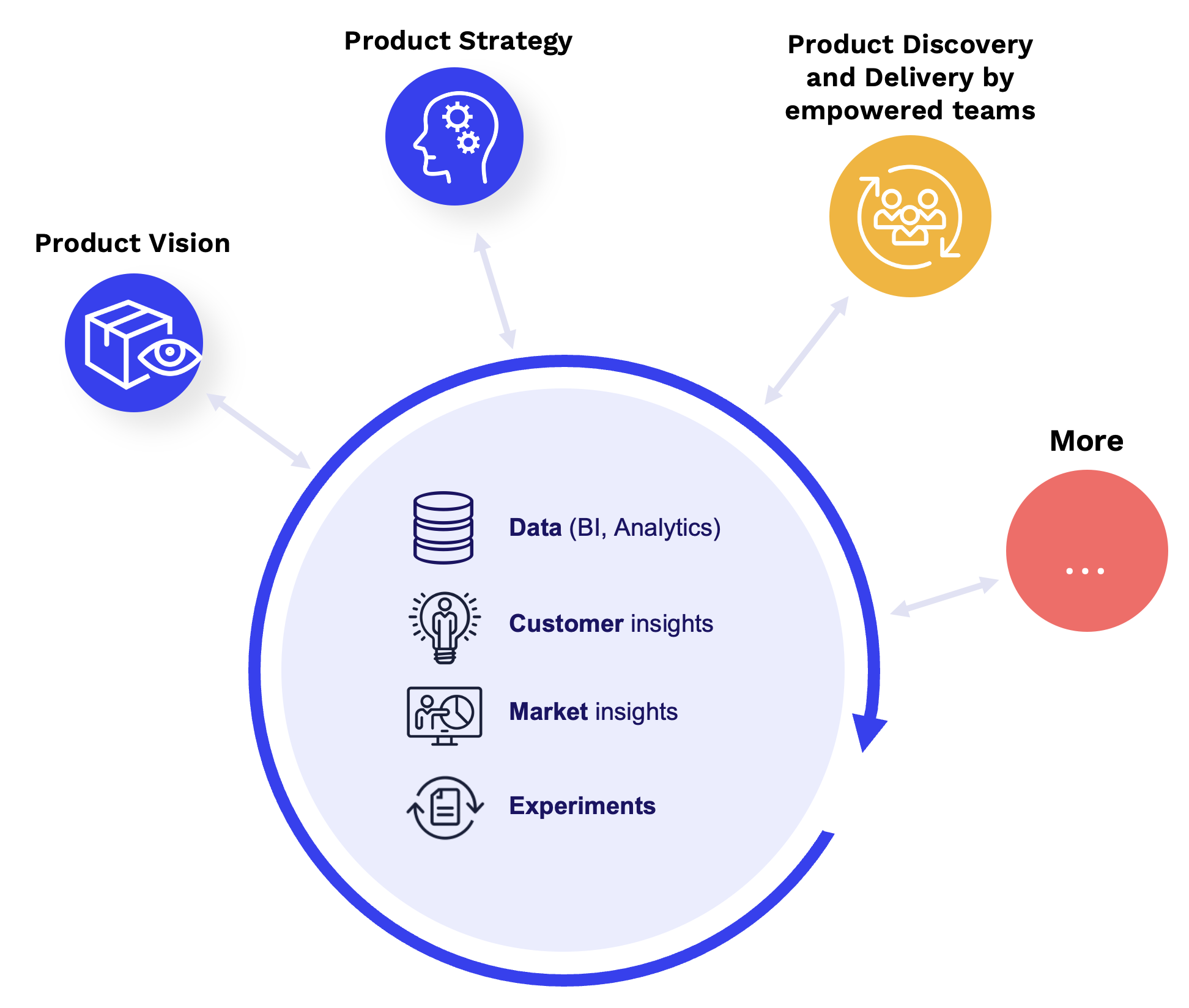
1. Data & Business Intelligence (BI)
Business Intelligence (BI) plays a critical role in monitoring performance, identifying trends, and measuring success. A well-structured BI system provides real-time access to:
• Product usage metrics (e.g., active users, retention rates, churn)
• Sales and revenue insights
• Operational efficiency data
• Customer support trends and pain points
By making data easily accessible to everyone in the company, teams can make faster, informed decisions without relying on isolated reports or waiting for analysis.
2. Customer Insights
Understanding customer behavior is fundamental to product strategy. Insights can come from multiple sources, including:
• User interviews and feedback loops
• Behavioral analytics (heatmaps, session recordings, user flows)
• Surveys and Net Promoter Score (NPS)
• Customer support interactions
By continuously gathering and structuring these insights, product teams can anticipate customer needs, rather than simply reacting to requests.
3. Market Insights
A great product strategy also requires a deep understanding of the market. This includes:
• Competitive analysis (what others are doing, how they position themselves)
• Emerging industry trends (new technologies, regulatory changes, customer expectations)
• Shifts in user behavior (e.g., mobile-first adoption, privacy concerns)
Staying ahead of these trends helps businesses identify strategic opportunities before competitors do.
4. Experimentation & Continuous Learning
Insights alone aren’t enough—companies must test hypotheses and validate assumptions through experimentation. This includes:
• A/B testing (optimizing features, pricing, user flows)
• Prototyping & usability testing (before full-scale development)
• Pilot programs (testing new features with a small segment of users)
• Data-driven iteration (improving products based on real user feedback)
By making experimentation an ongoing process, teams ensure that product decisions are always evolving based on real-world learning.
Creating a Centralized Insights Hub
To make insights actionable, they must be easily accessible and structured. Many companies store insights within Product Operations, ensuring a continuous and collaborative approach to collecting and sharing data.
A centralized insights hub could be built in tools like:
• Figma boards (for visual organization)
• Notion, Confluence, or Miro (for structured documentation)
• Internal dashboards (for live data updates)
The key is to ensure that everyone in the company—across Product, Sales, Marketing, and Support—can access and contribute to these insights intuitively.
Conclusion
A successful product strategy is fueled by insights, not assumptions. By embedding data, customer behavior, market trends, and experimentation into everyday decision-making, companies can stay ahead of the competition and continuously innovate. The best teams don’t just react to customer requests—they anticipate needs, validate ideas, and refine solutions based on evidence.
By fostering a culture of insights-sharing and collaboration, product teams gain clarity, autonomy, and alignment—ensuring that every decision is driven by real value for customers and the business.